AWS Elastic MapReduce (EMR) is a cloud-based big data platform that simplifies the processing and analysis of large data sets. It provides a managed Hadoop framework that lets you process and analyze vast amounts of data using other frameworks like Apache Spark, HBase, Presto, and Flink. The architecture of AWS EMR is designed to be scalable, flexible, and integrated with various AWS services.
Key Components of AWS EMR Architecture
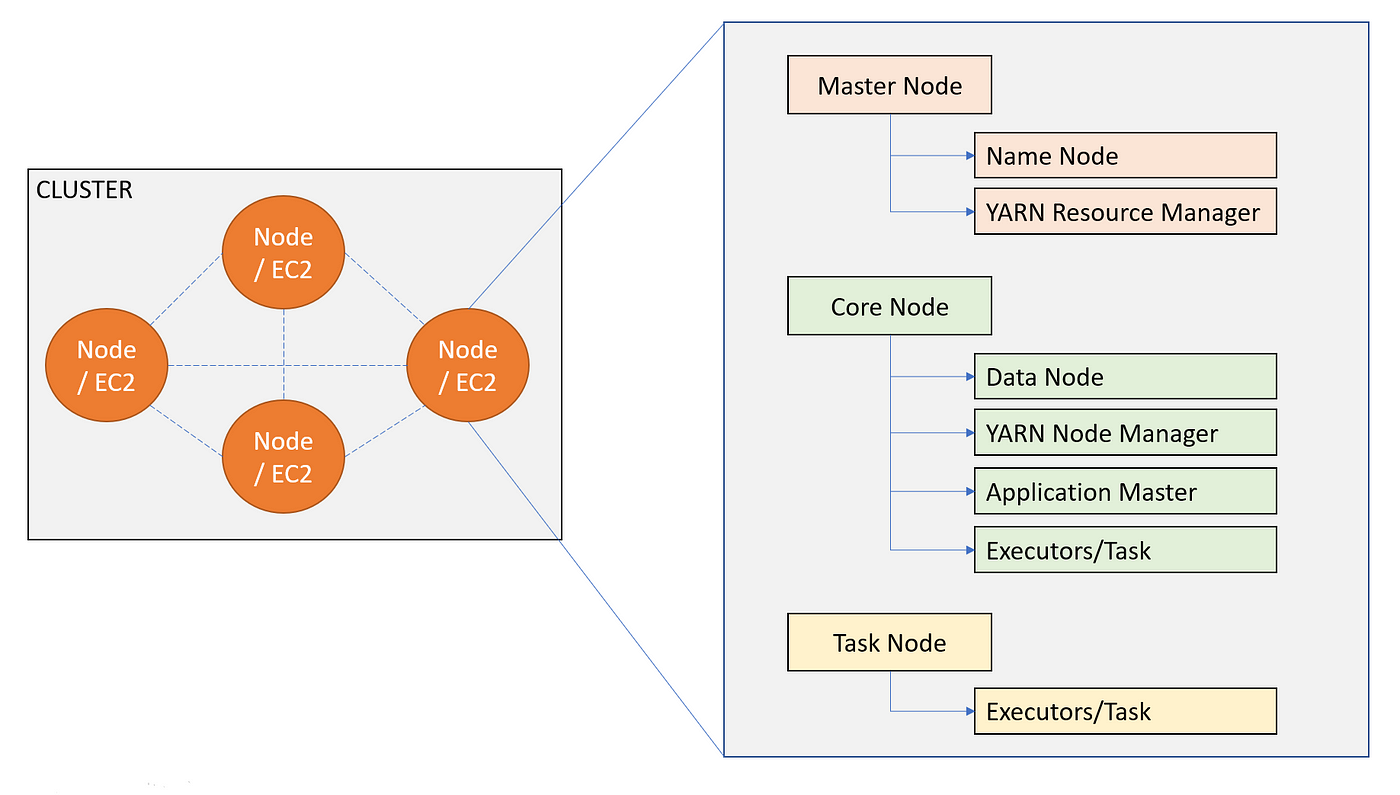
Cluster:
-
The core unit of EMR is a cluster. A cluster consists of one or more nodes, and each node runs its own instance of Hadoop or other supported frameworks.
-
A cluster typically has three types of nodes
-
Master Node: Manages the cluster by running the YARN ResourceManager and HDFS NameNode. It is responsible for coordinating the distributed processing of data.
-
Core Nodes: Run the YARN NodeManager and HDFS DataNode. They perform processing tasks and store data within the HDFS.
-
Task Nodes: Optional nodes that only run the YARN NodeManager. They do not store data but are used to increase processing capacity.
-
Data Storage:
-
Amazon S3: While EMR uses HDFS for temporary storage, Amazon S3 is commonly used for persistent storage. Data is often loaded from S3 into the cluster for processing and then written back to S3 after processing.
-
HDFS: Hadoop Distributed File System is used for storing data locally on the EMR nodes during processing.
-
Amazon EMRFS: An implementation of HDFS that allows EMR clusters to directly access data stored in S3.
Data Processing:
-
YARN: The resource management layer used in Hadoop. It allocates resources to various applications and schedules jobs across the cluster.
-
Apache Spark: A fast, in-memory data processing engine with high-level APIs for Java, Scala, Python, and R.
-
Apache Hadoop MapReduce: A framework for processing large data sets using a distributed algorithm on a cluster.
-
Apache HBase: A NoSQL database that runs on top of HDFS for real-time read/write access to large datasets.
-
Presto: A distributed SQL query engine optimized for low-latency, interactive queries.
-
Apache Flink: A stream processing framework used for real-time analytics.
Cluster Configuration and Management:
-
Amazon EC2 Instances: Each node in an EMR cluster runs on an Amazon EC2 instance. You can choose the instance types based on the workload requirements.
-
Auto Scaling: EMR clusters can automatically scale up or down based on resource needs, helping optimize cost and performance.
-
Instance Groups and Instance Fleets: These are configurations that define the type and number of EC2 instances used in the cluster.
Security:
-
IAM Roles and Policies: Control access to the cluster and its resources.
-
VPC: EMR can run inside an Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) for network isolation.
-
Kerberos Authentication: Can be enabled for secure authentication in the cluster.
Data Ingestion and Integration:
-
Amazon Kinesis: Stream data into EMR for real-time processing.
-
AWS Data Pipeline: Automates the movement and transformation of data.
-
AWS Glue: An ETL service that prepares data for analytics.