Apache Kafka is a distributed event streaming platform that is used for building real-time data pipelines and streaming applications. Here’s an overview of its architecture:
1. Producer
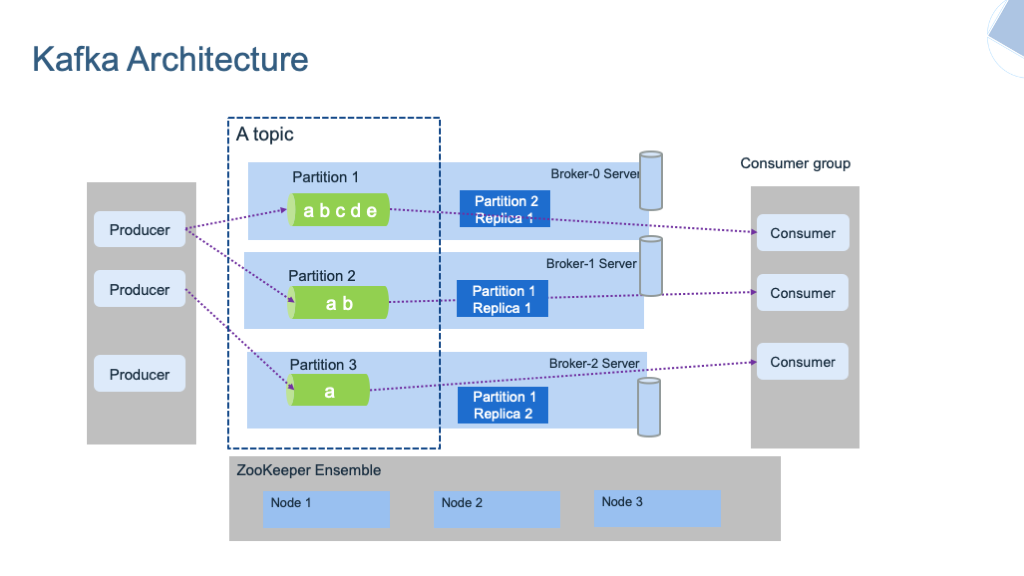
- Role: Producers are responsible for sending records (data) to Kafka topics. Each record consists of a key, value, timestamp, and optional metadata.
- Example: A web application generating logs can send each log entry to a Kafka topic.
2. Broker
- Role: Brokers are Kafka servers that store and serve data. Kafka clusters typically consist of multiple brokers.
- Partitioning: Topics in Kafka are divided into partitions, and each partition is replicated across multiple brokers. This ensures fault tolerance and scalability.
- Example: If a topic has three partitions and the cluster has three brokers, each broker could store one partition.
3. Topic
- Role: Topics are the categories in which records are stored. Each topic is split into partitions, and each partition is an ordered, immutable sequence of records.
- Retention: Kafka allows you to configure how long records are retained before being deleted.
- Example: You might have a “user-activity” topic for tracking user actions in an application.
4. Partition
- Role: Partitions are the basic unit of parallelism in Kafka. Records within a partition are stored in order, and consumers read from them sequentially.
- Replication: Each partition is replicated across multiple brokers to ensure availability. One of the replicas is the leader, and others are followers.
- Example: A topic with four partitions can handle four consumers reading from it in parallel.
5. Consumer
- Role: Consumers read records from Kafka topics. They can be part of a consumer group, where each consumer in the group reads from a different partition, ensuring parallel processing.
- Consumer Offset: Kafka keeps track of the last record read by each consumer, using a concept called “offset.”
- Example: An analytics system that processes logs could be a consumer of the “user-activity” topic.
6. Consumer Group
- Role: A consumer group is a set of consumers that share the work of consuming records from a topic. Each partition is consumed by only one consumer in the group.
- Load Balancing: Kafka automatically balances the load among consumers in a group.
- Example: If there are three consumers in a group and a topic with six partitions, each consumer might read from two partitions.
7. ZooKeeper
- Role: Apache Kafka uses ZooKeeper to manage and coordinate the Kafka brokers. ZooKeeper helps in maintaining the cluster’s metadata, leader election, and configuration.
- Transition: Kafka is transitioning to KRaft mode, which eliminates the need for ZooKeeper and brings native Kafka metadata management.
- Example: ZooKeeper keeps track of which broker is the leader for each partition.
8. Replication
- Role: Kafka ensures data durability and availability through replication. Each partition can be replicated across multiple brokers.
- Leader and Followers: One broker is the leader for a partition, and others are followers. The leader handles all reads and writes, while followers replicate the data.
- Example: If a broker fails, a follower can take over as the leader, ensuring no data loss.
9. Kafka Streams
- Role: Kafka Streams is a client library for building real-time applications that process data in Kafka. It allows you to process and analyze data stored in Kafka topics.
- Example: A real-time monitoring system could use Kafka Streams to aggregate and analyze log data.
10. Connectors
- Role: Kafka Connect is a tool for connecting Kafka with other data sources and sinks. It provides pre-built connectors for various databases, file systems, and other systems.
- Example: You could use Kafka Connect to stream data from a MySQL database into a Kafka topic.