In Apache Cassandra, a snitch is a component that determines the physical and network topology of the nodes within a cluster. It plays a crucial role in routing read and write requests, replica placement, and optimizing data replication by understanding the network’s topology. Here’s what a snitch does and why it’s important:
What a Snitch Is
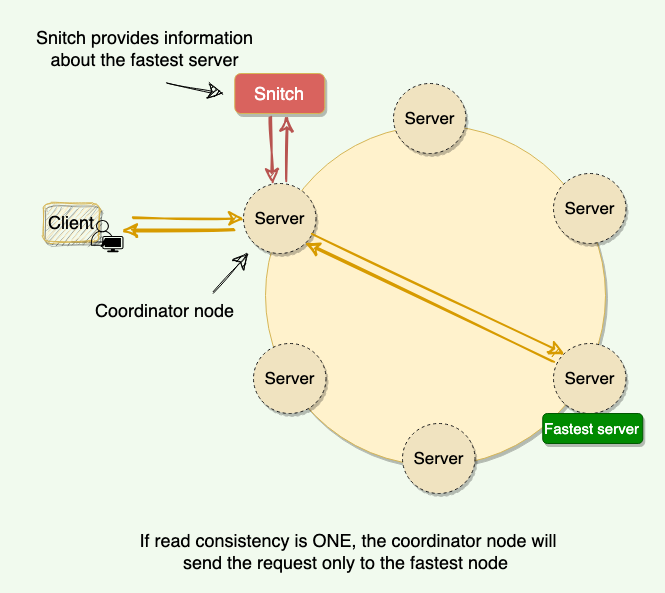
A snitch is a configuration component in Cassandra that provides information about the network topology and the relative proximity of nodes to each other. This information is used to optimize data distribution and request routing within the cluster.
Types of Snitches:
Cassandra provides several types of snitches, each tailored to different deployment environments and network configurations. Examples include:
-
SimpleSnitch:
Assumes all nodes are in the same datacenter and rack. It doesn’t consider any specific network topology and is suitable for small clusters or development environments.
-
GossipingPropertyFileSnitch:
Uses gossip to share the topology information across nodes, allowing for dynamic updates. It reads the initial topology from a configuration file and is commonly used in production environments.
What a Snitch Is For ?
-
Replica Placement:
The snitch informs Cassandra about the network topology, which it uses to place replicas in a way that balances fault tolerance and latency. For example, in a multi-datacenter setup, a snitch ensures that replicas are spread across different datacenters and racks to avoid a single point of failure.
-
Request Routing:
When a client requests data, the snitch helps determine the nearest replica (in terms of network proximity) to minimize latency. It influences how Cassandra routes read and write requests to optimize performance.
-
Consistency and Availability:
By understanding the network topology, a snitch helps Cassandra achieve the desired consistency level and availability. For instance, during a network partition, the snitch helps determine which nodes can still communicate and ensures that requests are routed to accessible replicas.
-
Optimizing Data Distribution:
Snitches enable Cassandra to distribute data efficiently across nodes, taking into account factors like latency, rack awareness, and datacenter proximity. This helps optimize the cluster’s performance and resilience.
-
Failover and Recovery:
In the event of a node failure, the snitch’s topology information helps Cassandra choose the best nodes for failover and recovery, ensuring minimal disruption and quick recovery.
Example Scenario
In a multi-datacenter deployment, you might use the GossipingPropertyFileSnitch, which will allow Cassandra to understand the datacenter and rack configuration of each node. This ensures that replicas are placed in different datacenters and racks, providing fault tolerance. When a client makes a read request, the snitch will help route the request to the closest replica, minimizing latency.
Summary
A snitch in Cassandra is a critical component for managing how data is replicated and accessed across the cluster, taking into account the network topology to optimize performance, consistency, and availability.