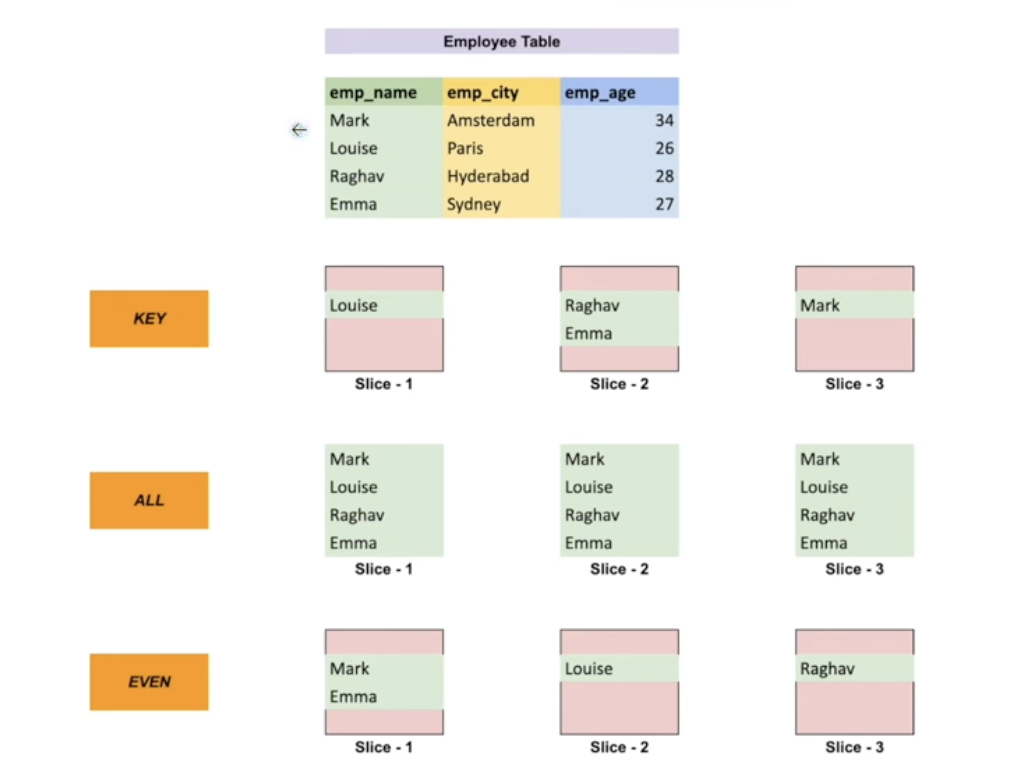
In Amazon Redshift, distribution style refers to how data is physically distributed across the compute nodes within a cluster. This distribution strategy is crucial for optimizing query performance and efficiently utilizing compute resources. There are three main distribution styles available in Amazon Redshift:
Even Distribution:
-
In an even distribution, also known as a round-robin distribution, data rows are distributed evenly across all compute nodes in the cluster.
-
This distribution style is useful when there is no clear column that could serve as a good distribution key. It ensures that the data is spread evenly across all nodes, which can help in achieving balanced query performance across the cluster.
-
However, it may not be optimal for performance if queries often join tables based on a common key because it could result in data redistribution during query execution.
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column1 datatype,
column2 datatype,
...
)
DISTSTYLE EVEN;
Key Distribution:
-
Key distribution, also called distribution by key, involves selecting a specific column (or set of columns) as the distribution key.
-
Rows with the same distribution key value are hashed to the same compute node. This ensures that rows that are frequently joined together are physically collocated on the same node, reducing the need for data redistribution during query execution.
-
Key distribution is beneficial for optimizing join performance but requires careful consideration of the distribution key to avoid data skew (where one node handles significantly more data than others).
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column1 datatype,
column2 datatype,
...
)
DISTKEY (column_name);
All Distribution:
- All distribution, also known as replication or distribution style all, involves making a complete copy of the entire table on every compute node.
- This distribution style is suitable for small dimension tables or lookup tables that are frequently joined with larger fact tables. It ensures that all compute nodes have a local copy of the data, eliminating the need for data redistribution during joins.
- It can improve query performance for small tables but increases storage requirements, as each node stores a full copy of the table.
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column1 datatype,
column2 datatype,
...
)
DISTSTYLE ALL;