Amazon Redshift is a fully managed data warehouse service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS), designed to handle large-scale data analytics workloads. Its architecture is optimized for high performance and scalability. Here are the key components and aspects of Amazon Redshift architecture:
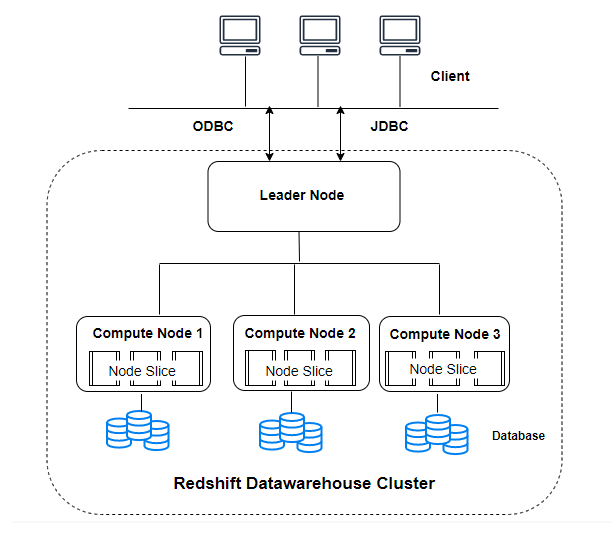
Clusters:
-
The fundamental unit of computation and storage in Amazon Redshift is the cluster. A cluster consists of a leader node and multiple compute nodes.
-
Leader Node: Manages communications with client applications, receives queries, creates execution plans, and coordinates the parallel execution of queries across compute nodes.
-
Compute Nodes: Store data and perform computations and transformations. Each compute node runs an instance of the Amazon Redshift engine and manages a portion of the overall data.
Columnar Storage:
-
Amazon Redshift stores data in a columnar format rather than row-based. This is optimized for analytical queries that typically involve scanning large volumes of data but retrieving only a subset of columns.
-
Columnar storage reduces I/O overhead and improves query performance by minimizing the amount of data read from disk.
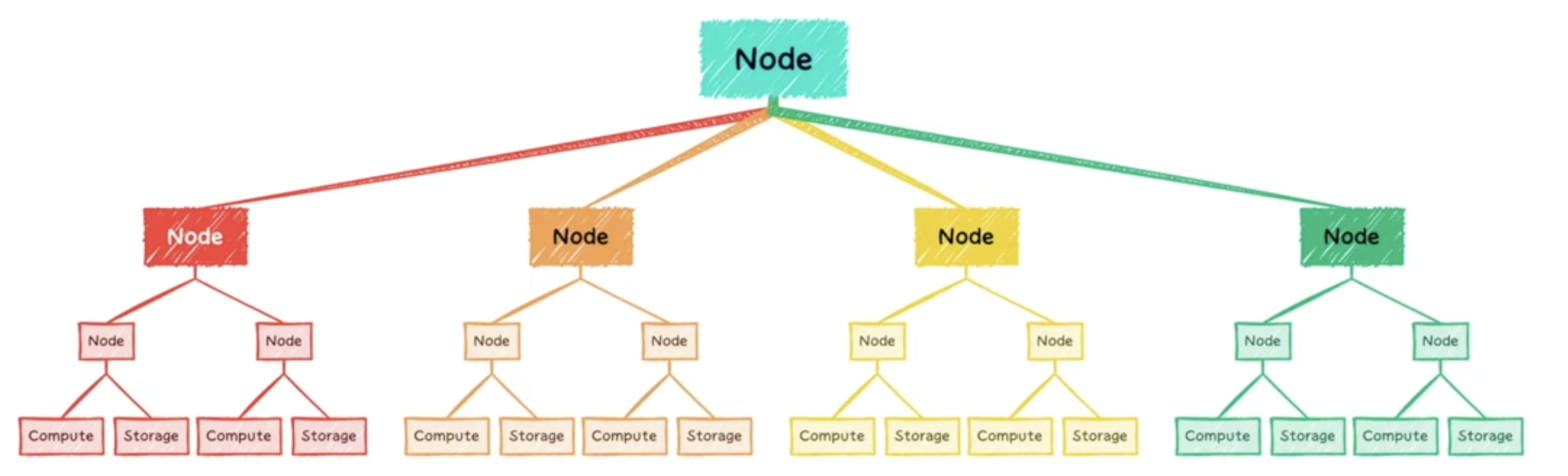
Massively Parallel Processing (MPP)
- DIVIDE THE WORK INTO SMALL ‘SIMILAR’ TASKS
- INDIVIDUAL TEAMS WORK IN SILO TO COMPLETE THE TASK
- DIRECTOR COLLATE THE TASKS BACK INTO ONE
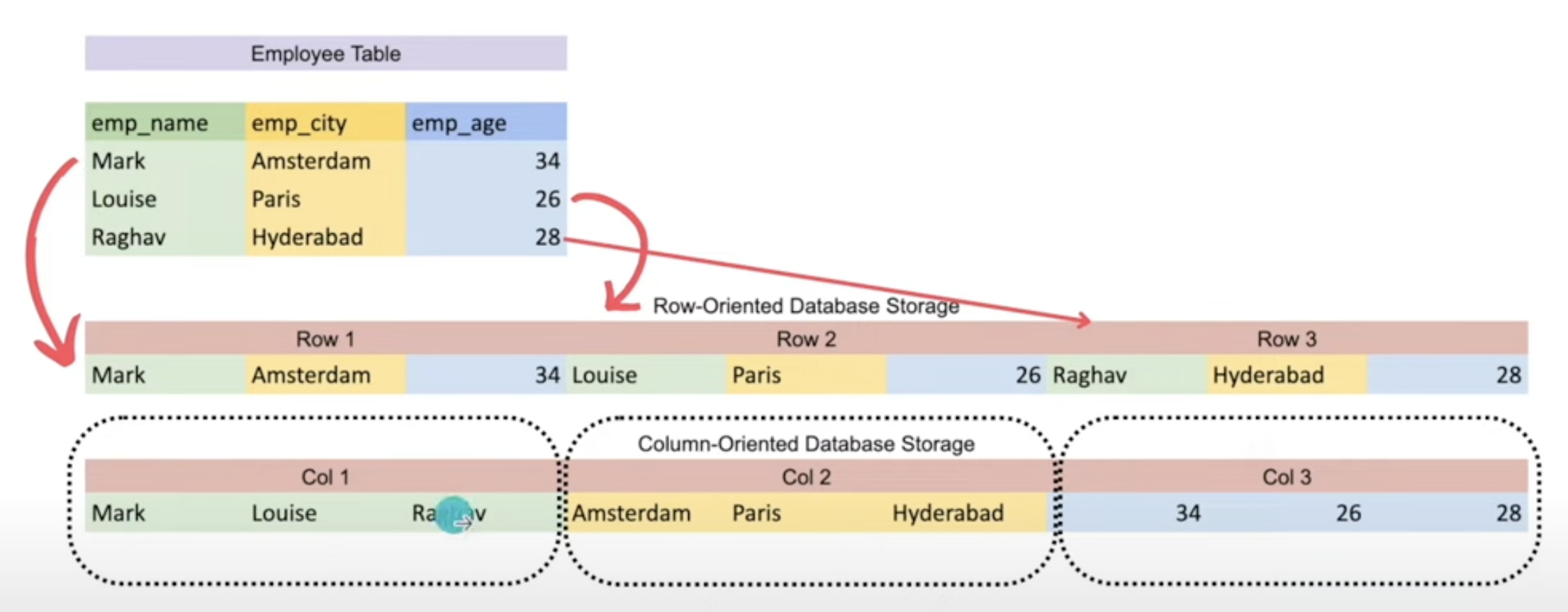
Columnar Database
- COLUMNS ARE STORED IN SAME/ADJACENT
- EFFICIENT READ WHEN FEW COLUMNS ARE REQUIRED
- BETTER COMPRESSION AT COLUMN LEVEL