Terraform modules are a fundamental concept in Terraform, a popular infrastructure-as-code tool developed by HashiCorp. Modules help organize and reuse code for creating and managing infrastructure resources. Here’s a breakdown of what Terraform modules are and how they work:
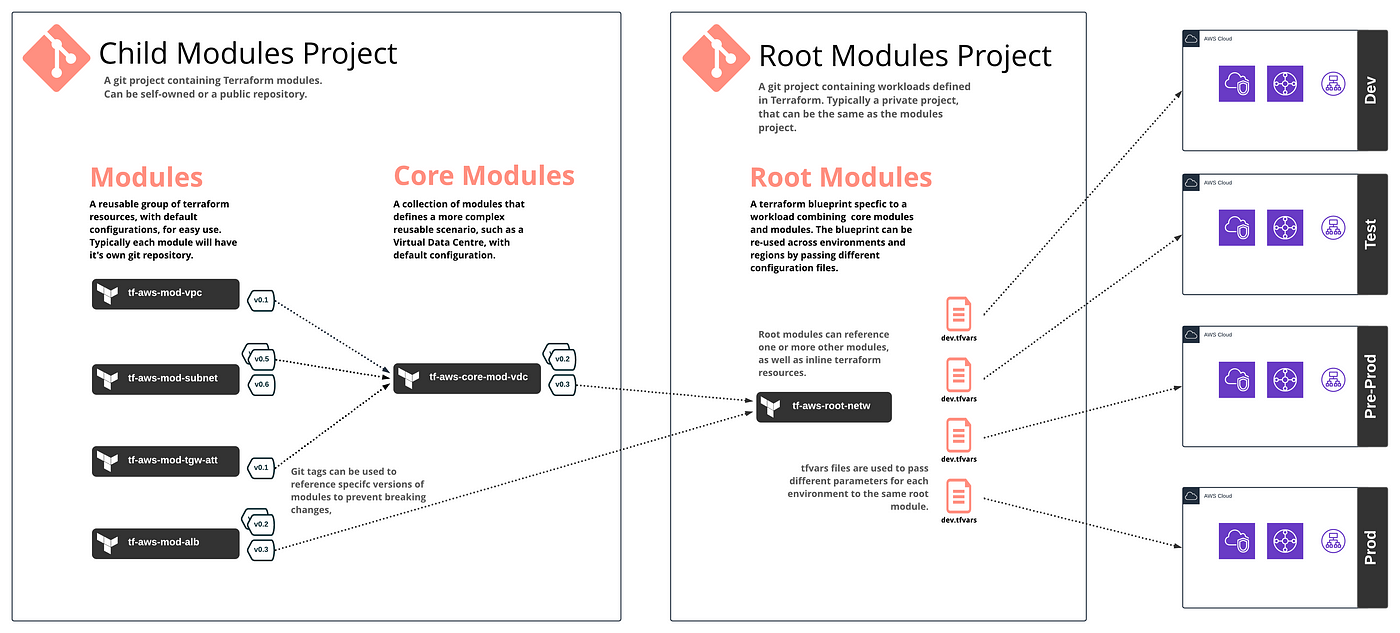
What is a Terraform Module?
-
Definition:
- A Terraform module is a container for multiple resources that are used together. It allows you to encapsulate and abstract a set of resources and their configuration into a reusable and manageable unit.
-
Structure:
- A module typically contains:
main.tf: Defines the primary resources and their configurations.variables.tf: Specifies the input variables for the module.outputs.tf: Defines the output values that other configurations can use.providers.tf: (Optional) Specifies providers needed by the module.
- A module typically contains:
-
Types of Modules:
- Root Module: The configuration in the main working directory where you execute
terraform apply. This module includes all the Terraform configurations in that directory. - Child Modules: Modules that are called by other modules (which can be either root or other child modules). These modules are usually located in separate directories and referenced by the root or other modules.
- Root Module: The configuration in the main working directory where you execute
Benefits of Using Modules
-
Reusability:
- Modules allow you to reuse code across multiple configurations. For example, if you have a module to create an AWS VPC, you can use that same module in different environments (like staging and production) with different configurations.
-
Maintainability:
- By encapsulating related resources into a module, you can manage and update them in one place. This makes your Terraform configuration more modular and easier to maintain.
-
Organization:
- Modules help in organizing complex configurations by breaking them into smaller, more manageable pieces. This improves readability and makes it easier to understand and manage your infrastructure.
-
Consistency:
- Using modules helps ensure consistent configurations across different environments and projects. Since the module code is reused, you reduce the risk of discrepancies and errors.
How to Use a Module
-
Create a Module:
- Define a module by creating a directory with the necessary
.tffiles (e.g.,main.tf,variables.tf,outputs.tf).
- Define a module by creating a directory with the necessary
-
Call a Module:
- Use the
moduleblock in your root configuration to call and use the module. For example:
- Use the
module "my_vpc" {
source = "./modules/vpc"
vpc_name = "my-vpc"
cidr_block = "10.0.0.0/16"
}
-
Source:
- The
sourceargument in themoduleblock specifies the location of the module. This can be a local path (like./modules/vpc), a Git repository, or a Terraform Registry.
- The
-
Pass Variables:
- Provide values for the module’s input variables when calling it. These variables are defined in
variables.tfwithin the module.
- Provide values for the module’s input variables when calling it. These variables are defined in
-
Use Outputs:
- Access the outputs defined in the module by referencing them in your root configuration. For example:
output "vpc_id" {
value = module.my_vpc.vpc_id
}
Example
Here’s a simple example of how you might define and use a module:
Module Directory (modules/vpc/main.tf):
resource "aws_vpc" "this" {
cidr_block = var.cidr_block
tags = {
Name = var.vpc_name
}
}
Module Variables (modules/vpc/variables.tf):
variable "vpc_name" {
type = string
}
variable "cidr_block" {
type = string
}
Root Configuration (main.tf):
module "my_vpc" {
source = "./modules/vpc"
vpc_name = "my-vpc"
cidr_block = "10.0.0.0/16"
}
In summary, Terraform modules are a powerful way to structure and manage your infrastructure code, allowing for better organization, reusability, and maintainability.